gr-remotecar 使用GNURadio控制遥控小车
gr-remotecar
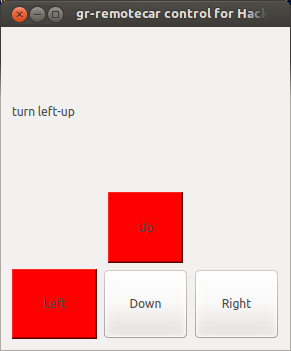
I wrote a GNURadio module to generate control signal for toy remote controlled car, and a Qt(PySide) GUI to listen keyboard press.
detail and source code:
http://github.com/scateu/gr-remotecar
Video DEMO
INSTALL
mkdir build
cd build
make
sudo make install
sudo ldconfig
TRY
refer to examples/
examples/WheelPulse/Wheel.py is a simple PySide based controller which you can control your toy car with keyboard direction keys. And it is for RemoteCarIIBaseBand
Just replay it.
on examples/tx.sh and examples/rx.sh , I demo how to capture the car’s remote signal and just replay it. And it turns out to make the car run.
cd examples
./rx.sh car.iq
./tx.sh car.iq
and it means:
hackrf_transfer -t car.iq -f 27000000 -s 8000000 -a 1 -l 30 -i 30 -x 40
27000000 is for 27MHz, you may find the frequency sign on you car’s remote.
Principle
We support two kind of remote car control :
RemoteCarBaseBand
-->|TIME3 |<-- TIME4
--------+ +-------+ +-------+ +--------- ... -------+ +---.....
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
+----+ +----+ +----+ +----+
TIME0 TIME0 TIME0
-->| TIME2 |<---
TIME0 = 520us
TIME3 = 300us to 1.3ms
TIME4 = 300us to 1.3ms
TIME2 = 20ms
TIME3 and TIME4 control car’s accelerator and direction.
RemoteCarIIBaseBand
+----------+ +----------+ +----------+ +----------+ +-----+ +-----+
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
+ +-----+ +-----+ +-----+ +-----+ +-----+ +-...
|<- 3t ->| t |<- 3t ->| t |<- 3t ->| t |<- 3t ->| t | t | t | t |
and we can simply capture it with HackRF using a AM demode gnuradio-companion workflow.
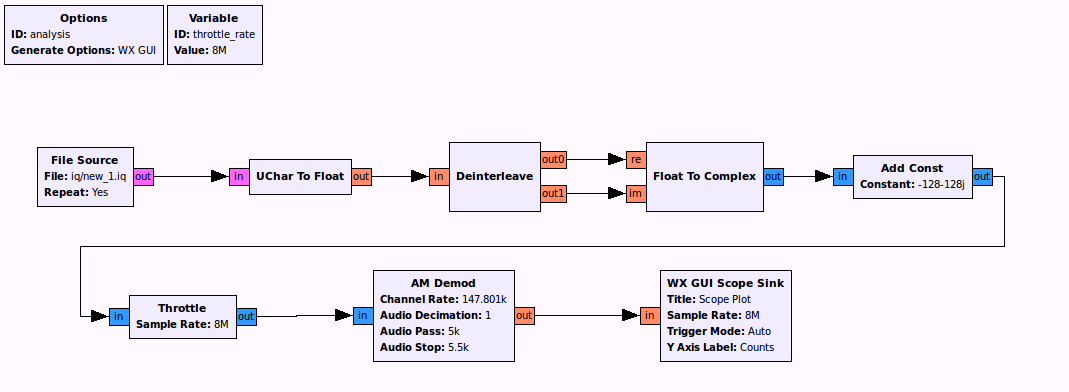
it is on examples/analysis.grc
Left: n=58
Right: n=64
Forward: n=10
Fast Forward: n=22
Backward: n=40
Left Forward: n=28
Right Forward: n=34
Left Backward: n=46
Right Backward: n=52
t = 0.55 ms
and you can try it with examples/WheelPulse/Wheel.py
遥控小车的信号分析与生成
直接重放
首先使用频谱仪或者查资料获知其频率在27.145MHz, 所以我们取中心频率为27MHz, 以8M采样率采回16M个点, 时长2秒
hackrf_transfer -r car.iq -f 27000000 -s 8000000 -n 16000000
重放, 注意优化它的发射增益
hackrf_transfer -t car.iq -f 27000000 -s 8000000 -a 1 -l 30 -i 30 -x 40
使用GNURadio对采集到的iq进行分析
控制信号分析结果
27.145MHz的遥控小车的信号大致可以认为是如下的PPM/AM波形:
PPM意为Pulse Position Modulation, 脉冲位置调制
TIME3 TIME4
--------+ +---------+ +-------+ +--------- ... -------+ +---.....
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
+----+ +----+ +----+ +----+
TIME0 TIME0 TIME0
-->| TIME2 |<---
其中的典型值为
TIME0 = 520us
TIME2 = 20ms
TIME3,TIME4 = [300us,1.3ms]
TIME3的时间长度控制了小车的左右
TIME4的时间长度控制了小车的油门量
用Python生成基带进行原理验证
import struct
SAMP_RATE=8e6
TIME_TOTAL = int(1 * SAMP_RATE) #s
TIME0 = int(520e-6 * SAMP_RATE)
TIME10 = int(300e-6 * SAMP_RATE)
TIME11 = int(1.3e-3 * SAMP_RATE)
TIME2 = int(20e-3 * SAMP_RATE)
Control0 = 0 #[0,1] 0.5 = stop orientation
Control1 = 1#speed
TIME3 = (TIME11-TIME10) * Control0 + TIME10
TIME4 = (TIME11-TIME10) * Control1 + TIME10
TIME_REST = TIME2-TIME0*3-TIME3-TIME4
MIN=struct.pack('B',128)
MAX=struct.pack('B',255)
def WriteFrame(value,quantity,f):
j = 0
while j < quantity:
f.write(value) #i
f.write(value) #q
j += 1
def main():
f = open('w.iq','wb')
i = 0
WriteFrame(MAX,1e-3*SAMP_RATE,f)
i += 1e-3*SAMP_RATE
while i < TIME_TOTAL:
WriteFrame(MIN,TIME0,f)
i += TIME0
WriteFrame(MAX,TIME3,f)
i += TIME3
WriteFrame(MIN,TIME0,f)
i += TIME0
WriteFrame(MAX,TIME4,f)
i += TIME4
WriteFrame(MIN,TIME0,f)
i += TIME0
WriteFrame(MAX,TIME_REST,f)
i += TIME_REST
f.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
然后生成了w.iq的原始基带数据.
如何查看它是否正确呢? 让我们打开gnuradio-companion来做出一个简单的信号流程来调试一下.
写GNURadio模块: 第二种车
信号原理分析
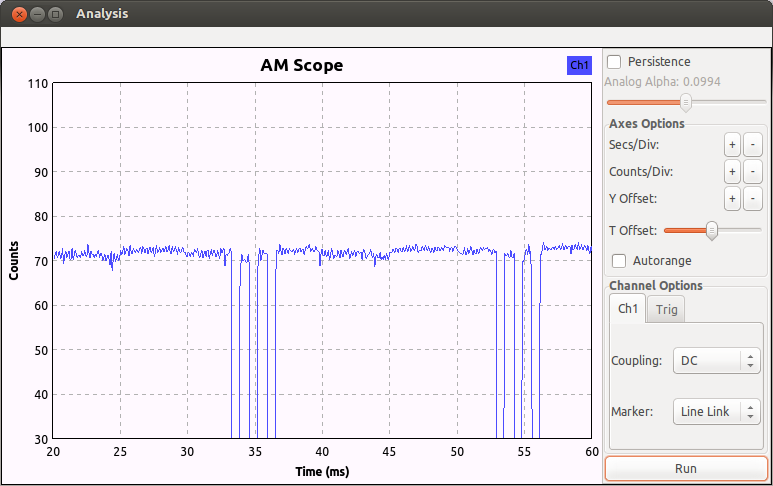
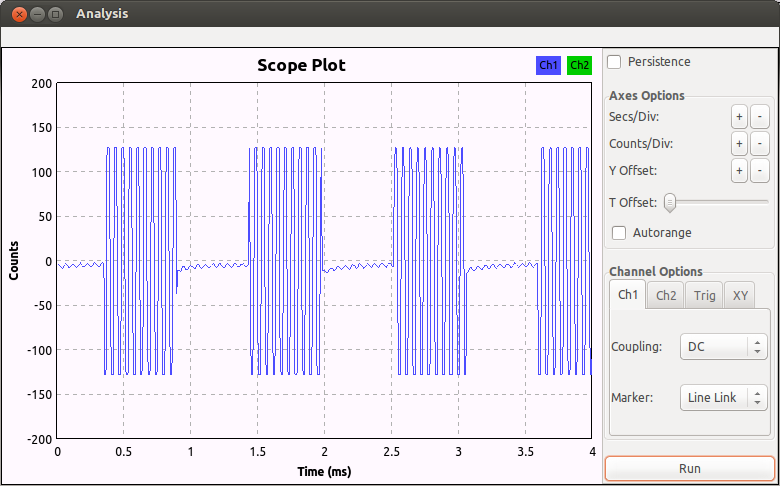
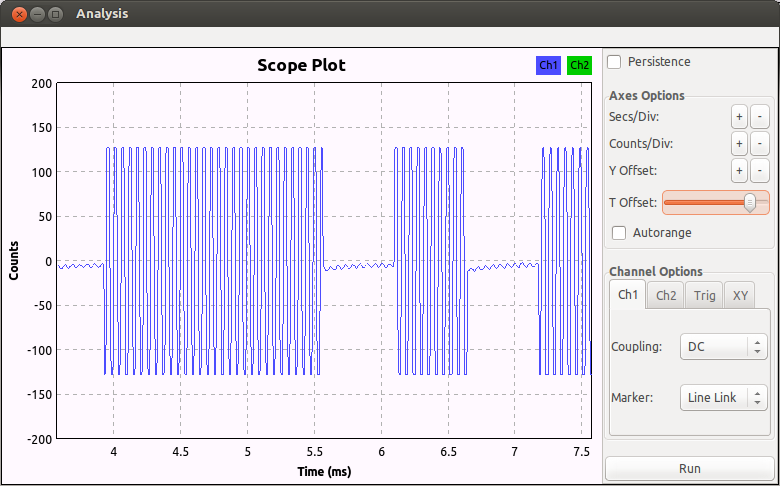
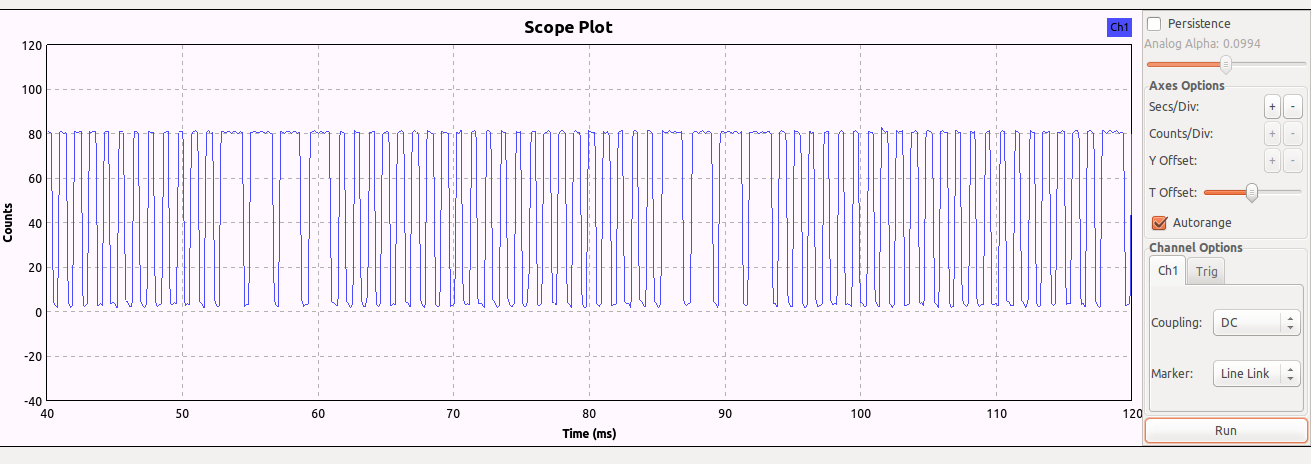
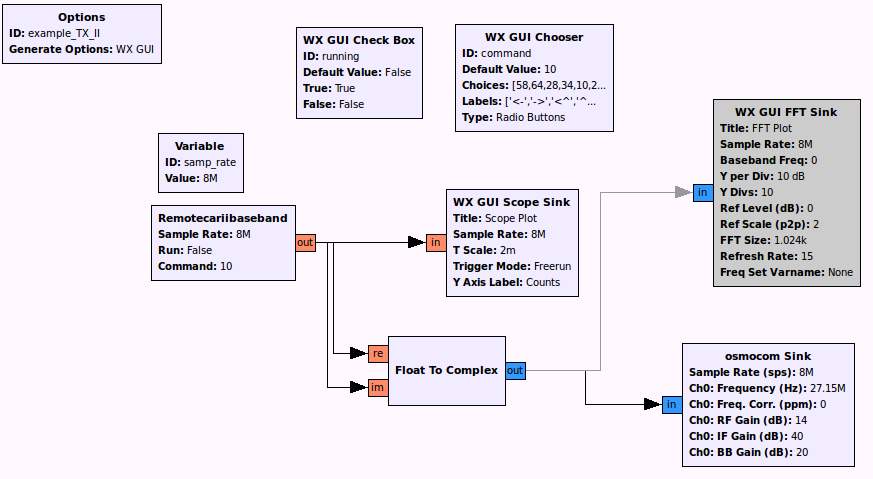
使用gnuradio-companion搭建AM解调, 然后输出到WX GUI Scope Sink里, 发现信号在27MHz是如下情形:
+----------+ +----------+ +----------+ +----------+ +-----+ +-----+
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
+ +-----+ +-----+ +-----+ +-----+ +-----+ +-...
|<- 3t ->| t |<- 3t ->| t |<- 3t ->| t |<- 3t ->| t | t | t | t |
每个控制帧都由4个长脉冲和n个短脉冲组成
经过测试, 找到n的值如下:
左: n=58
右: n=64
1档前进: n=10
2档前进: n=22
后退: n=40
1档左前: n=28
1档右前: n=34
左后: n=46
右后: n=52
模块建立
$ gr_modtool new remotecar
$ gr_modtool add RemoteCarIIBaseBand -t sync
GNU Radio module name identified: remotecar
Language: C++
Block/code identifier: RemoteCarIIBaseBand
Enter valid argument list, including default arguments: double samp_rate,bool run, int command
Add Python QA code? [Y/n] n
Add C++ QA code? [Y/n] n
Adding file 'RemoteCarIIBaseBand_impl.h'...
Adding file 'RemoteCarIIBaseBand_impl.cc'...
Adding file 'RemoteCarIIBaseBand.h'...
Editing swig/remotecar_swig.i...
Adding file 'remotecar_RemoteCarIIBaseBand.xml'...
Editing grc/CMakeLists.txt...
写io_signature
在lib/RemoteCarIIBaseBand_impl.cc文件中:
RemoteCarIIBaseBand_impl::RemoteCarIIBaseBand_impl(double samp_rate,bool run, int command)
: gr::sync_block("RemoteCarIIBaseBand",
gr::io_signature::make(0,0,0),
gr::io_signature::make(1,1,sizeof(float)))
添加所需变量
在lib/RemoteCarBaseBand_impl.h里加入
namespace gr {
namespace remotecar {
class RemoteCarIIBaseBand_impl : public RemoteCarIIBaseBand
{
private:
double d_samp_rate;
bool bool_run;
int n_pre;
int n_command;
int current_pre;
int current_command;
int current_sample_index;
public:
RemoteCarIIBaseBand_impl(double samp_rate,bool run, int command);
~RemoteCarIIBaseBand_impl();
// Where all the action really happens
int work(int noutput_items,
gr_vector_const_void_star &input_items,
gr_vector_void_star &output_items);
};
} // namespace remotecar
} // namespace gr
....
work
整个类的生命周期内一直存在,
GNURadio的调度器会调用work函数, 索取noutput_items个结果
生成grc
$ gr_modtool makexml RemoteCarIIBaseBand
GNU Radio module name identified: remotecar
Warning: This is an experimental feature. Don't expect any magic.
Searching for matching files in lib/:
Making GRC bindings for lib/RemoteCarIIBaseBand_impl.cc...
Overwrite existing GRC file? [y/N] y
grc中On Off的设置
参考: gnuradio/gr-wxgui/grc/wxgui_scopesink2.xml
<block>
<name>Remotecariibaseband</name>
<key>remotecar_RemoteCarIIBaseBand</key>
<category>REMOTECAR</category>
<import>import remotecar</import>
<make>remotecar.RemoteCarIIBaseBand($samp_rate,$run, $command)</make>
<param>
<name>Sample Rate</name>
<key>samp_rate</key>
<type>real</type>
</param>
<param>
<name>Run</name>
<key>run</key>
<value>True</value>
<type>bool</type>
<option>
<name>Off</name>
<key>False</key>
</option>
<option>
<name>On</name>
<key>True</key>
</option>
</param>
<param>
<name>Command</name>
<key>command</key>
<type>int</type>
</param>
<source>
<name>out</name>
<type>float</type>
</source>
</block>
Stage 1通关测试
int
RemoteCarIIBaseBand_impl::work(int noutput_items,
gr_vector_const_void_star &input_items,
gr_vector_void_star &output_items)
{
float *out = (float *) output_items[0];
for (int i = 0;i < noutput_items; i++){
out[i] = 1.5;
}
// Tell runtime system how many output items we produced.
return noutput_items;
}

加入基带信号生成部分
在lib/RemoteCarBaseBand_impl.cc里加入代码
RemoteCarIIBaseBand_impl::RemoteCarIIBaseBand_impl(double samp_rate,bool run, int command)
: gr::sync_block("RemoteCarIIBaseBand",
gr::io_signature::make(0,0,0),
gr::io_signature::make(1,1,sizeof(float)))
{
bool_run = run; // output on off
d_samp_rate = samp_rate;
n_command = command; // command code
n_pre = 4; // pre pulse number
current_command = 0;
current_pre = 0;
current_sample_index = 0;
}
...
int
RemoteCarIIBaseBand_impl::work(int noutput_items,
gr_vector_const_void_star &input_items,
gr_vector_void_star &output_items)
{
float *out = (float *) output_items[0];
for (int i = 0;i < noutput_items; i++){
if (bool_run) {
if (current_pre < n_pre) {
if (current_sample_index < d_samp_rate * 0.00055 * 3) {
out[i] = 1;
current_sample_index += 1;
}
else if (current_sample_index < d_samp_rate * 0.00055 * 4){
out[i] = 0;
current_sample_index += 1;
} else { // a long pre pulse generated.
current_sample_index = 0;
current_pre += 1;
}
}
else if (current_command < n_command) {
// 4 pre long pulse generated, then generate other short pulse.
if (current_sample_index < d_samp_rate * 0.00055 ) {
out[i] = 1;
current_sample_index += 1;
}
else if (current_sample_index < d_samp_rate * 0.00055 * 2){
out[i] = 0;
current_sample_index += 1;
} else { // a short command pulse generated
current_sample_index = 0;
current_command += 1;
}
}
else {
// 1 frame generated
current_pre = 0;
current_command = 0;
current_sample_index = 0;
}
} else { // muted
out[i] = 0;
}
}
// Tell runtime system how many output items we produced.
return noutput_items;
}
回调函数
如果没有回调函数, 那么生成的模块不能在gnuradio-companion里被WX GUI Slider实时的修改参数.
为了能够实时地控制小车, 我们需要加入两个回调函数.
在lib/RemoteCarBaseBand_impl.h里加入set_run和set_command函数的声明
namespace gr {
namespace remotecar {
....
// Where all the action really happens
int work(int noutput_items,
gr_vector_const_void_star &input_items,
gr_vector_void_star &output_items);
void set_run(bool run);
void set_command(int command);
};
} // namespace remotecar
} // namespace gr
....
还需要在include/remotecar/RemoteCarIIBaseBand.h加入set_run和set_command的声明
class REMOTECAR_API RemoteCarIIBaseBand : virtual public gr::sync_block
{
public:
typedef boost::shared_ptr<RemoteCarIIBaseBand> sptr;
static sptr make(double samp_rate,bool run, int command);
virtual void set_run(bool run) = 0;
virtual void set_command(int command) = 0 ;
};
在lib/RemoteCarIIBaseBand_impl.cc里加入set_run和set_command的实现
void RemoteCarIIBaseBand_impl::set_run(bool run) {
bool_run = run;
}
void RemoteCarIIBaseBand_impl::set_command(int command) {
n_command = command;
}
最后, 在grc/remotecar_RemoteCarIIBaseBand.xml文件里加入
<make>remotecar.RemoteCarIIBaseBand($samp_rate,$run, $command)</make>
<callback>set_run($run)</callback>
<callback>set_command($command)</callback>
....
编译
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ../ && make && sudo make install && sudo ldconfig
然后重启gnuradio-companion即可看到效果